"M&A Valuation Guide" 6: Global AI M&A Wave Resurges: China and the US Lead, Algorithms and Winner-Take
The 10 selected representative cases (5 domestic and 5 international) all focus on China and the United States. This not only reflects the two nations' leading positions globally in AI technology R&D, capital resources, and industrial implementation but also implies that a 'bipolar landscape' in current AI innovation and competition is gradually taking shape.
1. Algorithms as the Core Arena, Tech R&D Becomes a Capital Consensus
9 out of the 10 cases focus on algorithms (including algorithm + hardware): Domestic examples include LiblibAI (AI multimodal creation), Moonshot AI (general large models), Astribot (cable-driven robotics algorithms); International cases include OpenAI (AGI), Anthropic (large models + AI safety), Anysphere (Cursor, AI programming tools), etc. They cover cutting-edge directions like multimodal AI, embodied intelligence, and foundation models, highlighting the underlying 'technology-driven' logic of the AI industry. Algorithm R&D has become key for companies to build core competitive moats.
2. Winner-Take-All Effect Intensifies, Extreme Valuation Divergence
The valuation range presents a 'pyramid-shaped structure': 4 projects have valuations below $10 billion (e.g., Moonshot AI at $3.8B, Reflection AI at $8B); while the 2 projects with valuations exceeding $300 billion are both US companies (OpenAI at $300B, Anthropic at $350B). This confirms the 'concentration at the top' in global AI financing — incomplete market statistics indicate that the top 5% of projects valued over $1 billion attracted 58% of the funds. Leading companies, leveraging technological moats and ecosystem advantages, occupy the high ground for resources, further widening the gap with smaller players.
3. Computing Power as a Shared Focus, Divergence in Development Stages and Capital Nature Between Regions
Computing power is a core strategic area for both China and the US: Domestically, Wu Wen Xin Qiong (Uni-Win Tech) raised nearly 500 million RMB in its Series A+ round, managing 25,000 PetaFLOPs of computing power. Internationally, the US company Cerebras secured $1.1 billion in its Series G round, deepening its focus on AI computing hardware R&D.
Regarding differences, all 5 domestic projects are in the growth stage (e.g., Stardust Intelligence's A++ round, LiblibAI's Series B), focusing on scenario implementation (e.g., Stardust Intelligence's 'Robot MART', Leju Robotics delivering 100 humanoid robots to BAIC), with deep involvement from government-backed industrial funds (e.g., Zhuhai Sci-Tech Industrial Group leading the investment in Wu Wen Xin Qiong). In contrast, the 5 US companies are predominantly in mature stages (e.g., Anysphere securing $2.3B in an undisclosed round), mainly targeting global market expansion, with capital led by market-oriented institutions like Iconiq and SoftBank.
This disparity reflects both the pragmatic path of 'technology implementation' in China's AI sector and the strategic layout of 'ecosystem expansion' by leading US companies. The dual focus on computing power and algorithms will continue to define the competitive barriers in the global AI industry.
2025 also marked an explosive period for AI M&A. According to incomplete market statistics, global transaction volume increased by 35%. China accounted for 18% of the deals, ranking second globally (with the United States being first), and led the way with a 32% valuation premium.
This article analyzes 6 representative cases (3 domestic, 3 international), revealing the following core trends:
1. Computing Power + Talent: The Consistent Global Theme in M&A
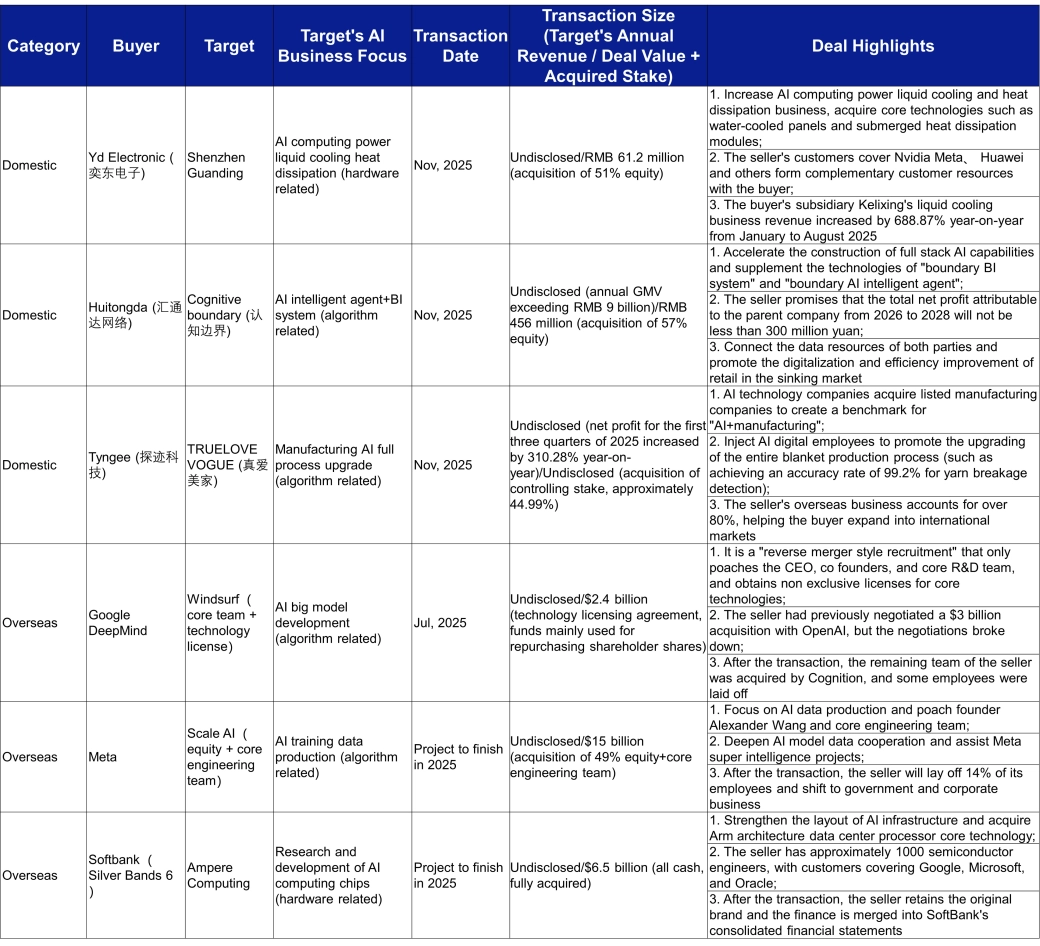
Both domestic and international strategies converge on "computing hardware + core talent":
On the computing power front, with a 60% performance boost in domestic AI chips and surging demand, Yd Electronic acquired a 51% stake in Shenzhen Guanding for 61.2 million RMB. This move secures AI computing liquid cooling technology, as the target company's clients include NVIDIA and Huawei, helping to position in the infrastructure sector. Internationally, SoftBank fully acquired Ampere Computing for $6.5 billion, gaining Arm-based AI chip technology and its 1,000-engineer team serving Google and Microsoft, thereby strengthening its AI hardware ecosystem.
On the talent front, the "technology + team" acquisition model accounted for 38% of deals. Domestically, Huitongda Network acquired a 57% stake in Cognitive Boundary for 456 million RMB, primarily to obtain its "AI agent + BI system" technology and team. The target boasts an annual GMV exceeding 9 billion RMB, aiding the digitalization of retail in lower-tier markets. Internationally, Google DeepMind acquired the core team of Windsurf for $2.4 billion, recruiting its CEO and key R&D personnel to rapidly enhance its large model capabilities in the AGI field.
2. Significant Divergence in Domestic vs. International M&A Paths
Domestically, the focus is on "AI + Real Economy" integration. A prime example isTyngee Technology acquiring a 44.99% controlling stake in TRUELOVE VOGUE. By deploying AI digital employees, it achieved a full-process upgrade in blanket production, increasing broken yarn detection accuracy to 99.2%. The target's net profit for the first three quarters of 2025 surged by 310.28% year-on-year. Furthermore, leveraging the target's overseas business share of over 80%, it facilitates the global application of its AI technology. Yd Electronic's acquisition of Shenzhen Guanding also aims to empower AI infrastructure with computing hardware technology to serve real industry needs.
Internationally, the emphasis is on building a technological closed-loop. Meta acquired a 49% stake in Scale AI for $15 billion, recruiting its founder and core engineering team to complete its AI training data production capabilities, supporting full-stack R&D for super-intelligence projects. Google DeepMind's acquisition of Windsurf specifically targeted the CEO and core large model R&D team, aiming to quickly fill AGI capability gaps through technology licensing, solidify underlying technological barriers, and strengthen its core competitiveness in the AI race.
An analysis of current transactions and capital dynamics in the AI industry reveals two core characteristics in 2025:
- On the financing front, the winner-take-all effect is pronounced — globally, financing deals valued over $1 billion account for only 5% of the total number of projects but attracted 58% of the capital. In the United States, targets like OpenAI and Anthropic saw valuations surpass $300 billion. Domestically, growth-stage projects primarily focus on scenario implementation, with significant participation from government-backed industrial funds.
- On the M&A front, the transaction logic centers on "computing power + technical teams". Domestically, deals primarily revolve around "AI + real economy" integration, such as Tyngee's controlling stake in TRUELOVE VOGUE leading to a 310% growth in manufacturing net profit, and Yetd Electronic's acquisition of Shenzhen Guanding to secure a position in computing hardware. Internationally, the focus leans toward building a technological closed-loop, with companies like Meta and SoftBank using M&A to enhance capabilities in areas such as data and chips. Deals following the "technology + team" model accounted for 38% of transactions.
- Looking ahead, we will continue to monitor developments in AI industry financing and M&A, including shifts in transaction activity for computing hardware and Agent technology, the implementation outcomes of domestic industrial integration targets in sectors like "AI + Manufacturing/Healthcare", and emerging trends in cross-domain integration projects such as AI + IoT and Quantum Computing.