SRB annual work programme 2026
| Core business |
| Governance, organisation and tools |
| Talent management |
These priorities reflect a clear shift from planning to execution under SRM Vision 2028. Each priority is attached to a specific sub-area within these strategic pillars, ensuring that operational actions are fully aligned with long-term objectives. The goal is simple yet ambitious: make resolvability a reality through rigorous testing, streamlined governance and strengthened organisational resilience.
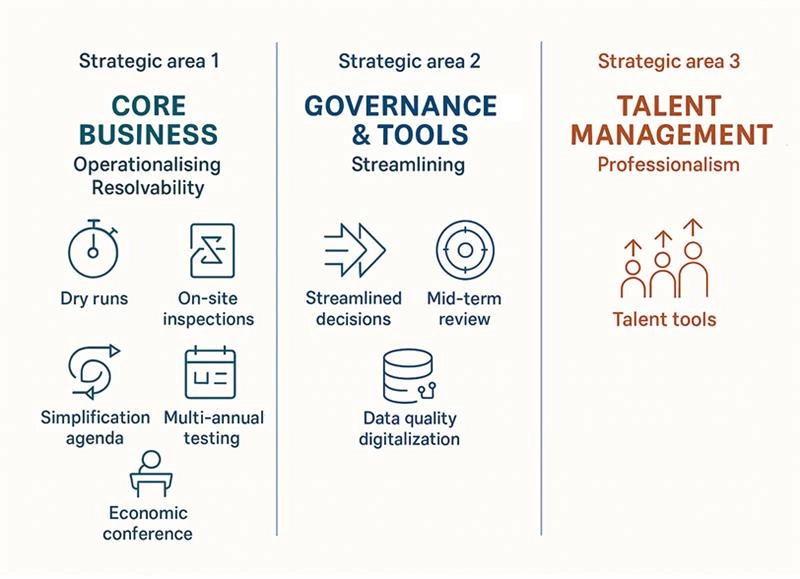
Strategic area 1: core business – operationalising resolvability
The SRB’s core mandate is to ensure banks can be resolved effectively under stress. In 2026, this translates into six priorities grouped under three sub-areas:
Crisis preparedness and management
1. Carry out revamped resolvability assessment and dry runs
The SRB will apply its updated methodology to assess resolvability and conduct dry runs simulating real crisis scenarios. These exercises will test operational readiness and identify gaps in banks’ resolution capabilities.
Resolution focused on crises and resolvability
2. Increase on-site inspections (OSIs)
OSIs will intensify, allowing the SRB and national risk assessments (NRAs) to verify compliance and readiness on the ground. This hands-on approach ensures that theoretical plans translate into practical capabilities.
SRB as a reference in resolution
3. Support simplification and competitiveness agenda simplification
Remains a priority to reduce complexity in resolution planning while maintaining robustness. This aligns with broader EU objectives for competitiveness and efficiency.
4. Implement the newly developed multi-annual testing framework
The SRB will operationalise its multi-annual testing programme, embedding resolvability checks into the supervisory cycle and ensuring consistent progress across institutions.
5. Convene the first economic conference
By hosting its inaugural conference, the SRB aims to foster dialogue on resolution policy, competitiveness and financial stability, reinforcing its role as a thought leader.
Strategic area 2: governance, organisation and tools – streamlining and digitalising
Efficient governance and robust data infrastructure are essential for rapid crisis response. Three sub-areas define this strategic pillar:
Strengthened governance and streamlined structure
6. Streamline decision-making processes
The SRB will simplify governance workflows to enhance agility, ensuring that critical decisions can be taken swiftly under stress.
Strong organisational culture and values
7. Perform the strategy mid-term review
At the halfway point of SRM Vision 2028, the SRB will assess progress, recalibrate objectives, and ensure alignment with evolving market and regulatory conditions.
Digital transformation and technology use
8. Execute data quality framework digitalisation
Central to operational efficiency. The SRB will accelerate its data quality framework, improving data governance and enabling faster data-driven decisions during crises.
Strategic area 3: talent management – building organisational resilience
People are at the heart of execution. The SRB will invest in talent and culture through:
Talent pool and professionalism
9. Continue developing talent management tools
Initiatives will focus on mobility, leadership development and skills enhancement to sustain organisational resilience and foster a strong SRM culture.
Why these priorities matter
The 2026 programme signals a pivot from design to deployment. By embedding resolvability testing, strengthening governance and leveraging digital tools, the SRB aims to ensure that resolution strategies are credible and executable under real-world stress conditions. This proactive stance is critical to safeguarding financial stability and reinforcing confidence in the banking union.
Key takeaways
· Operational readiness: dry runs, OSIs and multi-annual testing will dominate the agenda.
· Governance and efficiency: mid-term review, simplification and streamlined decision-making will enhance agility.
· Innovation and talent: digitalisation and human capital development will underpin long-term resilience.